[TOC]
一般来说都是通过 主从复制(Master-Slave)的方式来同步数据,再通过读写分离(MySQL-Proxy)来提升数据库的并发负载能力 这样的方案来进行部署与实施的。
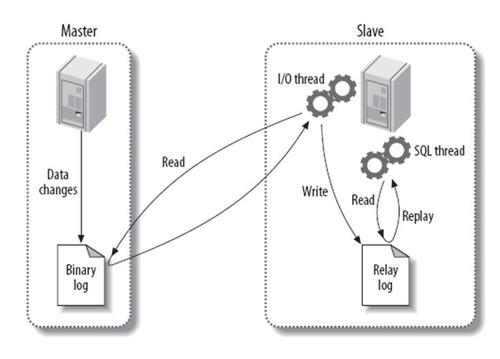
主从同步概述 MySQL主备复制原理
MySQL master 将数据变更写入二进制日志( binary log, 其中记录叫做二进制日志事件binary log events,可以通过 show binlog events 进行查看)
MySQL slave 将 master 的 binary log events 拷贝到它的中继日志(relay log)
MySQL slave 重放 relay log 中事件,将数据变更反映它自己的数据
主从同步数据库配置-Linux 1.打开mysql数据库配置文件 2.在主服务器master上配置开启Binary log 主要是在[mysqld]下面添加:
1 2 3 server-id=1 log-bin=master-bin log-bin-index=master-bin.index
3.重启mysql服务 1 sudo systemctl start mysqld.service
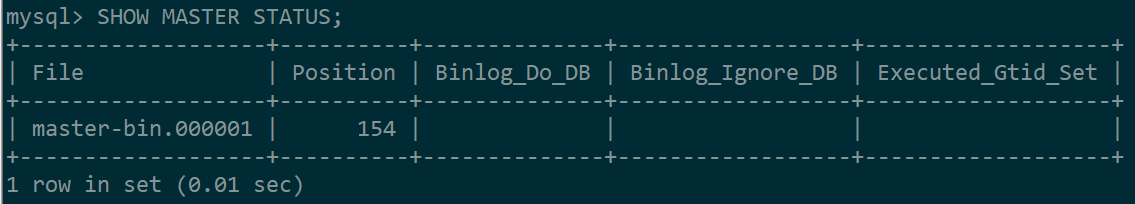
4.检查配置效果,进入主数据库并执行 1 mysql> SHOW MASTER STATUS;
可以看到下图表示配置没问题
这里面的File名:master-bin.000001 我们接下来在从数据库的配置会使用:
5.配置从服务器的 my.cnf 从服务器打开配置文件(vim /etc/my.cnf),在[mysqld]节点下面添加:
1 2 3 server-id=2 relay-log-index=slave-relay-bin.index relay-log=slave-relay-bin
配置完成之后重启
6.接下来配置两个数据库的关联 首先我们先建立一个操作主从同步的数据库用户
切换到主数据库 执行:
1 2 3 mysql> create user repl; mysql> GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'repl' @'192.168.60.131' IDENTIFIED BY '123456' ; mysql> flush privileges;
这个配置的含义就是创建了一个数据库用户repl,密码是123456, 在从服务器使用repl这个账号和主服务器连接的时候,就赋予其REPLICATION SLAVE的权限
. 表面这个权限是针对主库的所有表的,其中xxx就是从服务器的ip地址。
进入从数据库 后执行:
1 mysql> change master to master_host='xxx.xxx.xxx.xx(主服务器ip)' ,master_port=3306,master_user='repl' ,master_password='123456' ,master_log_file='master-bin.000001' ,master_log_pos=0;
这里面的xxx是主服务器ip,同时配置端口
repl代表访问主数据库的用户,上述步骤执行完毕后执行start slave启动配置:
停止主从同步的命令为:
查看状态命令,\G表示换行查看
1 mysql> show slave status \G
然后就可以看到从数据库已经在等待主库的消息了,接下来在主库的操作,在从库都会执行了。我们可以主库负责写,从库负责读(不要在从库进行写操作),达到读写分离的效果。
7.测试 在主数据库中创建一个新的数据库:
1 mysql> create database testsplit;
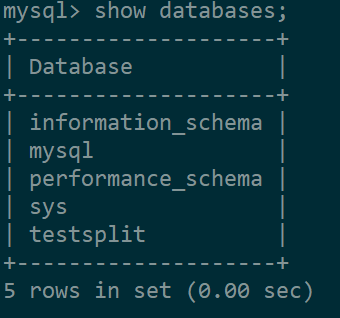
在从数据库查看数据库:
可以看到从数据库也有testsplit这张表了。另外,在主数据库插入数据,从数据库也可以查到。
到这里就完成了数据库的主从同步。
注意:
主从同步数据库配置-Docker
https://blog.csdn.net/fangkang7/article/details/105384477
中间件实现读写分离
代码层读写分离
https://www.jb51.net/article/129796.htm
上面我们已经有了两个数据库而且已经实现了主从数据库同步,接下来的问题就是在我们的业务代码里面实现读写分离,假设我们使用的是主流的ssm的框架开发的web项目,这里面我们需要多个数据源。
在此之前,我们在项目中一般会使用一个数据库用户远程操作数据库(避免直接使用root用户),因此我们需要在主从数据库里面都创建一个用户mysqluser,赋予其增删改查的权限:
1 mysql> GRANT select,insert,update,delete ON *.* TO 'mysqluser' @'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'mysqlpassword' WITH GRANT OPTION;
然后我们的程序里就用mysqluser这个用户操作数据库:
1.编写jdbc.propreties 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 jdbc.driver =com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.master.url =jdbc:mysql://xxx.xxx.xxx.xx:3306/testsplit?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8 jdbc.slave.url =jdbc:mysql://xxx.xxx.xxx.xx:3306/testsplit?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8 jdbc.username =mysqluser jdbc.password =mysqlpassword
这里我们指定了两个数据库地址,其中的xxx分别是我们的主从数据库的ip地址,端口都是使用默认的3306
2.配置数据源 在spring-dao.xml中配置数据源(这里就不累赘介绍spring的配置了,假设大家都已经配置好运行环境),配置如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" > <context:property-placeholder location ="classpath:jdbc.properties" /> <context:component-scan base-package ="com.liuurick.testsplit.dao" /> <bean id ="abstractDataSource" abstract ="true" class ="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" destroy-method ="close" > <property name ="maxPoolSize" value ="30" /> <property name ="minPoolSize" value ="10" /> <property name ="autoCommitOnClose" value ="false" /> <property name ="checkoutTimeout" value ="10000" /> <property name ="acquireRetryAttempts" value ="2" /> </bean > <bean id ="master" parent ="abstractDataSource" > <property name ="driverClass" value ="${jdbc.driver}" /> <property name ="jdbcUrl" value ="${jdbc.master.url}" /> <property name ="user" value ="${jdbc.username}" /> <property name ="password" value ="${jdbc.password}" /> </bean > <bean id ="slave" parent ="abstractDataSource" > <property name ="driverClass" value ="${jdbc.driver}" /> <property name ="jdbcUrl" value ="${jdbc.slave.url}" /> <property name ="user" value ="${jdbc.username}" /> <property name ="password" value ="${jdbc.password}" /> </bean > <bean id ="dataSourceSelector" class ="com.liuurick.testsplit.dao.split.DataSourceSelector" > <property name ="targetDataSources" > <map > <entry value-ref ="master" key ="master" > </entry > <entry value-ref ="slave" key ="slave" > </entry > </map > </property > </bean > <bean id ="dataSource" class ="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.LazyConnectionDataSourceProxy" > <property name ="targetDataSource" > <ref bean ="dataSourceSelector" > </ref > </property > </bean > <bean id ="sqlSessionFactory" class ="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean" > <property name ="dataSource" ref ="dataSource" /> <property name ="configLocation" value ="classpath:mybatis-config.xml" /> <property name ="typeAliasesPackage" value ="com.liuurick.testsplit.entity" /> <property name ="mapperLocations" value ="classpath:mapper/*.xml" /> </bean > <bean class ="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer" > <property name ="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value ="sqlSessionFactory" /> <property name ="basePackage" value ="com.liuurick.testsplit.dao" /> </bean > </beans >
说明: jdbc.properties,然后在我们定义了一个基于c3p0连接池的父类“抽象”数据源,然后配置了两个具体的数据源master、slave,继承了abstractDataSource,这里面就配置了数据库连接的具体属性,然后我们配置了动态数据源,他将决定使用哪个具体的数据源,这里面的关键就是DataSourceSelector,接下来我们会实现这个bean。下一步设置了数据源的懒加载,保证在数据源加载的时候其他依赖的bean已经加载好了。接着就是常规的配置了,我们的mybatis全局配置文件如下
3.mybatis全局配置文件 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd" > <configuration > <settings > <setting name ="useGeneratedKeys" value ="true" /> <setting name ="useColumnLabel" value ="true" /> <setting name ="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value ="true" /> <setting name ="logImpl" value ="STDOUT_LOGGING" /> </settings > <plugins > <plugin interceptor ="com.liuurick.testsplit.dao.split.DateSourceSelectInterceptor" > </plugin > </plugins > </configuration >
这里面的关键就是DateSourceSelectInterceptor这个拦截器,它会拦截所有的数据库操作,然后分析sql语句判断是“读”操作还是“写”操作,我们接下来就来实现上述的DataSourceSelector和DateSourceSelectInterceptor
4.编写DataSourceSelector DataSourceSelector就是我们在spring-dao.xml配置的,用于动态配置数据源。代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource;public class DataSourceSelector extends AbstractRoutingDataSource @Override protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey () return DynamicDataSourceHolder.getDataSourceType(); } }
我们只要继承AbstractRoutingDataSource并且重写determineCurrentLookupKey()方法就可以动态配置我们的数据源。DynamicDataSourceHolder,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 public class DynamicDataSourceHolder private static ThreadLocal<String> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<String>(); public static final String DB_MASTER = "master" ; public static final String DB_SLAVE = "slave" ; public static String getDataSourceType () String db = contextHolder.get(); if (db == null ){ db = DB_MASTER; } return db; } public static void setDataSourceType (String s) contextHolder.set(s); } public static void clearDataSource () contextHolder.remove(); } }
这个类决定返回的数据源是master还是slave,这个类的初始化我们就需要借助DateSourceSelectInterceptor了,我们拦截所有的数据库操作请求,通过分析sql语句来判断是读还是写操作,读操作就给DynamicDataSourceHolder设置slave源,写操作就给其设置master源,代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 import org.apache.ibatis.executor.Executor;import org.apache.ibatis.executor.keygen.SelectKeyGenerator;import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.BoundSql;import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement;import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.SqlCommandType;import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.*;import org.apache.ibatis.session.ResultHandler;import org.apache.ibatis.session.RowBounds;import org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionSynchronizationManager;import java.util.Locale;import java.util.Properties;@Intercepts ({@Signature (type = Executor.class ,method = "update" ,args = {MappedStatement.class ,Object .class }), @Signature (type = Executor.class ,method = "query" ,args = {MappedStatement.class ,Object .class , RowBounds .class , ResultHandler .class })}) public class DateSourceSelectInterceptor implements Interceptor private static final String REGEX = ".*insert\\\\u0020.*|.*delete\\\\u0020.*|.*update\\\\u0020.*" ; @Override public Object intercept (Invocation invocation) throws Throwable boolean synchonizationActive = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive(); Object[] objects = invocation.getArgs(); MappedStatement ms = (MappedStatement) objects[0 ]; String lookupKey = DynamicDataSourceHolder.DB_MASTER;; if (!synchonizationActive){ if (ms.getSqlCommandType().equals(SqlCommandType.SELECT)){ if (ms.getId().contains(SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX)){ lookupKey = DynamicDataSourceHolder.DB_MASTER; }else { BoundSql boundSql = ms.getSqlSource().getBoundSql(objects[1 ]); String sql = boundSql.getSql().toLowerCase(Locale.CHINA).replace("[\\t\\n\\r]" ," " ); if (sql.matches(REGEX)){ lookupKey = DynamicDataSourceHolder.DB_MASTER; }else { lookupKey = DynamicDataSourceHolder.DB_SLAVE; } } } }else { lookupKey = DynamicDataSourceHolder.DB_MASTER; } DynamicDataSourceHolder.setDataSourceType(lookupKey); return invocation.proceed(); } @Override public Object plugin (Object target) if (target instanceof Executor){ return Plugin.wrap(target,this ); }else { return target; } } @Override public void setProperties (Properties properties) } }
通过这个拦截器,所有的insert、delete、update操作设置使用master源,select会使用slave源。
接下来就是测试了,我这是生产环境的代码,直接打印日志,小伙伴可以加上日志后测试使用的是哪个数据源,结果和预期一样,这样我们就实现了读写分离~
注意 :我们可以配置多个slave用于负载均衡,只需要在spring-dao.xml中添加slave1、slave2、slave3……然后修改dataSourceSelector这个bean,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 <bean id="dataSourceSelector" class "com.liuurick.o2o.dao.split.DataSourceSelector" > <property name="targetDataSources" > <map> <entry value-ref="master" key="master"></entry> <entry value-ref="slave1" key="slave1"></entry> <entry value-ref="slave2" key="slave2"></entry> <entry value-ref="slave3" key="slave3"></entry> </map> </property>
在map标签中添加slave1、slave2、slave3……即可,具体的负载均衡策略我们在DynamicDataSourceHolder、DateSourceSelectInterceptor中实现即可。
最后整理一下整个流程:
总结 现在很多读写分离中间件已经大大简化了我们的工作,但是自己实现一个小体量的读写分离有助于我们进一步理解数据库读写分离在业务上的实现、、、